- Introduction
- What is AI Grading Software?
- Why It Matters: Key Benefits of AI Grading Software
- How AI Grading Software Works: Core Features & Functionality
- Real-Life Use Case: AI Grading in a High School English Class
- Top AI Grading Software & Automated Essay Scoring Tools in 2025: A Comparative Look
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing AI Grading Software
- Expert Tips & Best Practices for Maximizing AI Grading
- Frequently Asked Questions About AI Grading Software
- Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Assessment
Introduction
Picture this: stacks of papers, endless digital submissions, and the constant ticking clock. For teachers, grading is often the most time-consuming and exhausting part of their job, consuming precious evenings and weekends. In fact, a 2025 survey by the NEA highlighted that administrative work, including grading, is a top source of job-related stress for 29% of educators.
What if you could dramatically cut down on grading time, provide more consistent feedback, and reclaim those lost hours for teaching, planning, or simply, life? This guide will show you how AI grading software saves teachers hours weekly, revolutionizing the assessment process. By exploring these cutting-edge automated essay scoring tools and smart assessment solutions, you’ll discover how to streamline your workflow, offer richer feedback, and bring a new level of efficiency to your classroom in 2025.
What is AI Grading Software?
At its core, AI grading software refers to intelligent applications that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) to assist educators in evaluating student assignments. Far beyond simple auto-correct features, these tools employ sophisticated algorithms, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze student submissions against predefined rubrics, criteria, and even exemplary answers.
In 2025, the relevance of AI grading software is more pronounced than ever. With increasing class sizes, diverse learning needs, and the demand for prompt, personalized feedback, teachers are constantly seeking efficient solutions. AI steps in to fill this gap, offering a scalable way to manage the ever-growing assessment workload. Future trends point towards AI grading becoming even more adept at understanding context, identifying nuanced errors, and integrating seamlessly with personalized learning pathways.
Data from a 2025 study shows that AI marking tools have significantly reduced the time teachers spend on manual grading, cutting it by an average of 70%. This statistic, highlighting the transformative power of AI in education, comes from a comprehensive report on “AI in Education: Key Statistics for 2025” by All About AI, underscoring its growing adoption and impact.

Why It Matters: Key Benefits of AI Grading Software
The integration of AI grading software isn’t merely about adopting new technology; it’s about fundamentally enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the assessment process. These smart assessment solutions offer a multitude of benefits that directly address the challenges faced by today’s educators.
Automate Repetitive Grading Tasks
One of the most immediate and tangible advantages is the automation of mundane and time-consuming grading tasks. AI can swiftly evaluate objective assessments and even provide initial feedback on subjective ones.
- Instant Scoring for Quizzes: Automatically grades multiple-choice, true/false, and fill-in-the-blank questions, providing immediate results to students.
- Initial Draft Feedback: For essays and short answers, AI can identify grammatical errors, check for structural coherence, and flag areas where content is missing or unclear based on a rubric.
- Bulk Processing: Grades hundreds of submissions simultaneously, a task that would take human teachers days.
Provide Instant & Consistent Feedback
Timely and consistent feedback is crucial for student learning, but often a challenge due to teacher workload. AI grading software excels here.
- Immediate Learning Cycle: Students receive feedback almost instantly, allowing them to understand mistakes and improve while the material is still fresh in their minds.
- Unbiased Consistency: AI applies the same rubric and criteria uniformly to every student, eliminating human biases that can inadvertently affect grading.
- Detailed Explanations: Many tools can provide specific examples or explanations for why a certain score was given, guiding students toward improvement.
Enhance Assessment Fairness & Objectivity
Human grading, while nuanced, can sometimes be influenced by fatigue or unconscious biases. AI introduces a layer of objectivity that can lead to fairer assessments.
- Standardized Evaluation: Every submission is judged against the exact same digital rubric, ensuring a uniform evaluation process.
- Focus on Content: AI helps to minimize the impact of factors like handwriting, writing style (if not relevant to the rubric), or prior performance on current grading.
- Identification of Patterns: AI can highlight areas where a large number of students are struggling, indicating a potential need to review teaching methods.
Free Up Teacher Time for Deeper Engagement
Ultimately, the greatest benefit of AI grading software is not just efficiency, but the reallocation of a teacher’s most valuable resource: their time and expertise.
- Focus on Higher-Order Feedback: With basic grading handled, teachers can concentrate on providing qualitative, constructive feedback that targets critical thinking, creativity, and deeper understanding.
- Personalized Support: More time allows for one-on-one student conferences, targeted interventions, and differentiated support.
- Strategic Planning: Reduced grading burden means more energy for innovative lesson design and curriculum enhancement. For more strategies on optimizing educational practices, explore how AI can streamline administrative tasks in various sectors, including education.
How AI Grading Software Works: Core Features & Functionality
The sophistication of AI grading software lies in its ability to emulate human assessment processes through advanced computational methods. While the underlying AI models are complex, the user interaction is typically intuitive. Here’s a breakdown of the core features and functionality that define these automated essay scoring tools and smart assessment solutions.
- Rubric Definition and Training:
- Teacher Input: Educators define the specific criteria, weighting, and proficiency levels for an assignment, much like a traditional rubric.
- AI Learning: For subjective tasks like essays, the AI system is often “trained” with a set of human-graded examples. This allows it to learn patterns, identify key elements, and understand how human graders apply the rubric.
- Submission Processing & Analysis:
- Text Analysis (NLP): For written assignments, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is used to analyze grammar, syntax, vocabulary, coherence, argumentation, and relevance to the prompt.
- Pattern Recognition: For objective questions (e.g., math problems with defined answers), the AI uses pattern matching to quickly identify correct and incorrect responses.
- Code Analysis (for programming assignments): More advanced tools can even evaluate code for functionality, efficiency, and adherence to style guides.
- Score Generation & Feedback Delivery:
- Automated Scoring: Based on its analysis and the predefined rubric, the AI assigns a score to each component and a total grade.
- Contextual Feedback: The software generates specific feedback linked to rubric criteria. For an essay, this might include suggestions for stronger thesis statements, clearer topic sentences, or better evidence integration.
- Performance Insights: Teachers receive aggregated data, highlighting common errors across the class, areas of strength, and individual student progress.
- Teacher Override & Review:
- Human-in-the-Loop: Teachers always retain the ability to review AI-generated grades and feedback, making adjustments as needed. This “human-in-the-loop” approach ensures accuracy and addresses any limitations of the AI.
- Refinement: Teacher overrides can also be used to further train and improve the AI model over time, making it more accurate and aligned with the teacher’s specific grading style.
AI Grading Process Flow: From Submission to Insights
| Step | Description | AI’s Role | Teacher’s Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Setup Assignment | Teacher creates assignment, defines rubric/criteria. | Learns rubric, processes training data (if applicable). | Designs assignment, defines clear rubric and expectations. |
| 2. Student Submission | Students submit their work digitally. | Receives submissions, ready for analysis. | Ensures submission process is clear for students. |
| 3. AI Analysis & Scoring | AI evaluates submissions based on defined criteria. | Applies NLP/pattern recognition, generates scores and initial feedback. | Monitors process (optional), awaits results. |
| 4. Teacher Review & Refine | Teacher reviews AI’s output, provides final qualitative feedback. | Presents scores/feedback, learns from teacher overrides. | Adds personal comments, adjusts scores, focuses on higher-order feedback. |
| 5. Feedback to Students | Students receive grades and detailed feedback. | Delivers compiled feedback to individual students. | Interprets feedback with students, provides support. |
| 6. Data Analytics | AI provides insights into class performance trends. | Aggregates data, identifies common strengths/weaknesses. | Uses data to inform future instruction and support. |
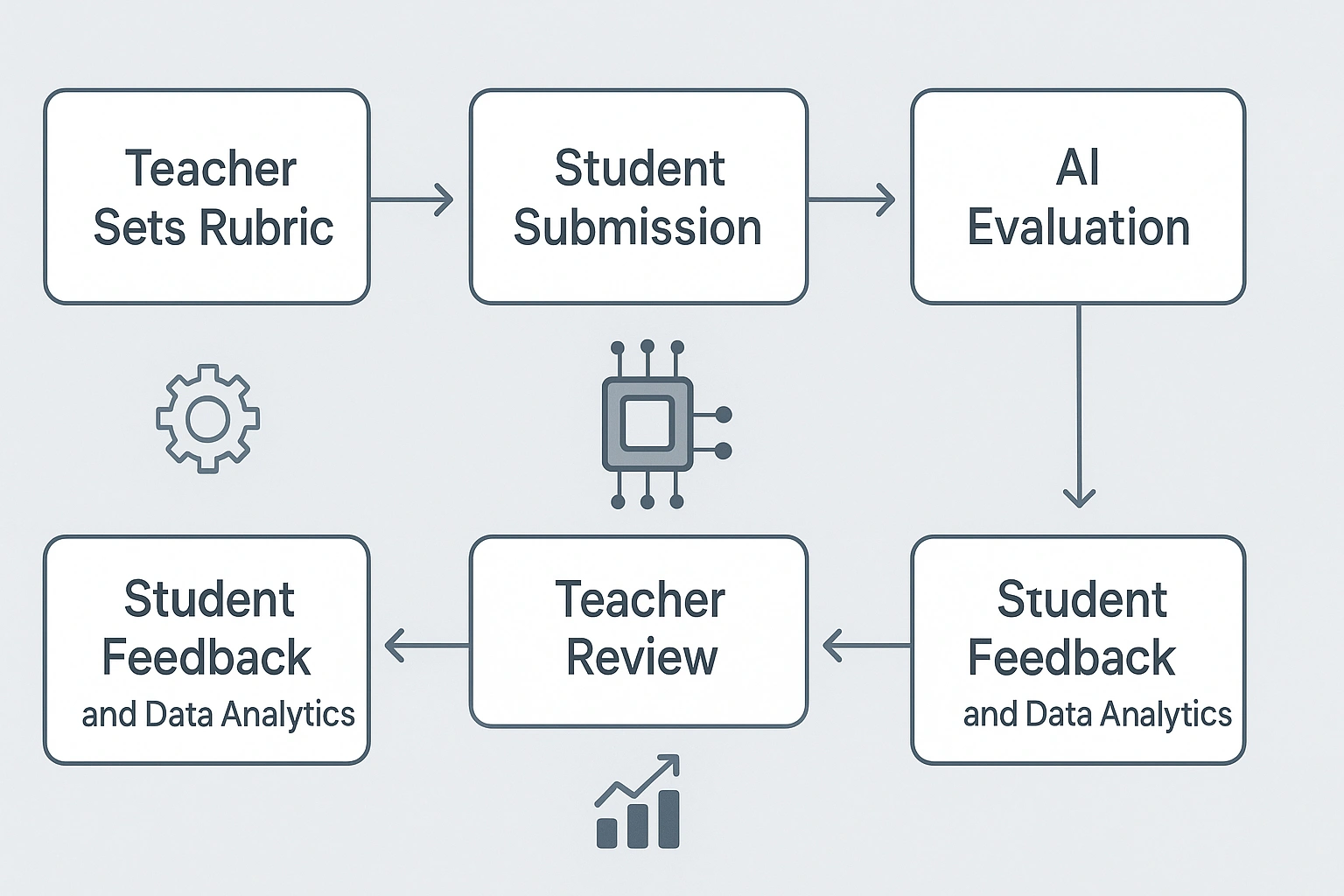
This systematic approach ensures that AI grading software acts as a powerful assistant, automating the heavy lifting while allowing teachers to maintain their essential human judgment and focus on nuanced feedback.
Real-Life Use Case: AI Grading in a High School English Class
Consider Mr. Evans, a busy 11th-grade English teacher, who assigns a persuasive essay to his three classes, totaling nearly 90 students. Historically, grading these essays would consume his entire weekend, leading to burnout and delayed feedback for students. This year, Mr. Evans integrated AI grading software into his workflow.
Before the assignment, he uploaded his essay rubric directly into the AI system, clearly defining criteria for thesis strength, evidence, organization, grammar, and style. Students submitted their essays digitally. Within minutes of the submission deadline, the AI had analyzed every essay.
The software provided an initial score for each criterion, highlighted grammatical errors, flagged areas needing stronger evidence, and even suggested improvements for sentence structure. Mr. Evans then spent a focused few hours reviewing the AI’s feedback. He used this foundation to add personalized, qualitative comments focusing on deeper analysis, creative expression, and individual student growth points—areas where human insight is irreplaceable.
“The difference is night and day,” Mr. Evans reflects. “I used to dread essay grading. Now, the AI handles the mechanical aspects, giving me a fantastic starting point. I can then dedicate my energy to what truly matters: guiding students to become better writers, not just finding every comma splice. My students also love the instant, consistent feedback; they can immediately see where they need to improve, rather than waiting days.” His students received detailed feedback within 24 hours, allowing them to apply lessons learned to their next assignment promptly.
Pros & Cons of Mr. Evans’ Experience with AI Grading
| Pros of AI Grading Software | Cons/Challenges |
|---|---|
| Significant Time Savings: Reduced grading hours from a weekend to a few focused hours. | Requires initial setup and training for specific rubrics. |
| Consistent & Objective Feedback: Ensures uniform application of rubric criteria. | May struggle with highly abstract or creative assignments without human oversight. |
| Faster Feedback Cycle: Students receive feedback quickly, improving learning. | Potential for algorithmic bias if training data is not diverse. |
| Highlights Common Errors: Provides data on class-wide strengths and weaknesses. | Requires teacher vigilance to prevent over-reliance or uncritical acceptance of AI suggestions. |
| Teacher Focus on Deeper Learning: Allows educators to concentrate on higher-order thinking and personalized guidance. | Integration with existing LMS systems might require technical support. |

This scenario highlights the practical utility of AI grading software in alleviating teacher workload and enriching the feedback process, ultimately benefiting both educators and students.
Top AI Grading Software & Automated Essay Scoring Tools in 2025: A Comparative Look
The market for AI grading software and automated essay scoring tools is rapidly expanding, with various solutions catering to different educational needs. Here’s a comparative overview of some popular hypothetical types that represent the leading edge of smart assessment solutions in 2025.
| Tool Category (Example) | Key Features | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “EssayGenius” (Automated Essay Scoring) | NLP-driven essay analysis, grammar/spelling checks, structural coherence feedback, rubric scoring, originality reports. | Excellent for detailed essay feedback, significant time savings for written assignments. | May struggle with highly creative or abstract writing; requires initial rubric setup. | English/Humanities teachers, large writing classes. |
| “QuizMaster AI” (Objective Assessment Grader) | Instant grading for MCQs, true/false, short answer; performance analytics, question bank integration. | Fastest grading for objective tests, immediate student feedback, robust data insights. | Limited use for subjective assessments, doesn’t provide deep qualitative feedback. | Math/Science teachers, large objective-based courses. |
| “CodeSensei” (Programming Assignment Grader) | Automated code compilation/execution, unit test integration, style guide adherence checks, syntax error identification. | Accurate and consistent code evaluation, provides immediate debugging feedback. | Requires technical knowledge to set up tests; may not fully assess logic/creativity without human review. | Computer Science/Programming instructors. |
| “Feedback Fusion” (Hybrid AI + Teacher Grading) | AI handles mechanical grading (grammar, structure), teacher adds personalized qualitative feedback; integrates with LMS. | Combines AI efficiency with human insight, optimal for rich feedback, flexible. | Still requires significant teacher time for the qualitative component; can be more complex to learn. | Teachers seeking balanced efficiency and personalized student interaction. |
| “Adaptive Assessor” (AI-Driven Diagnostic) | Grades based on mastery levels, identifies learning gaps, recommends personalized learning resources post-assessment. | Excellent for formative assessment, supports differentiated instruction, data-driven insights for teaching. | Primarily diagnostic, not a full summative grading tool; deeper integration may be required. | Educators focused on mastery learning and individualized student progression. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing AI Grading Software
While AI grading software promises significant advantages, its effective implementation hinges on avoiding common pitfalls. Being aware of these missteps will help you maximize the benefits of automated essay scoring tools and other smart assessment solutions.
- Blindly Trusting AI Output: Never assume AI-generated grades or feedback are flawless. Always review the results, especially for subjective assignments. AI is a tool, and your expert judgment remains indispensable.
- Neglecting Rubric Clarity and Specificity: AI grading is only as good as the rubric it follows. A vague or poorly defined rubric will lead to inconsistent or unhelpful feedback. Invest time in creating clear, detailed rubrics.
- Ignoring Data Privacy and Security: Student data is sensitive. Ensure the AI grading software you choose complies with all relevant privacy regulations (e.g., FERPA, GDPR) and has robust security measures. Avoid inputting personally identifiable student information into unverified tools.
- Failing to Personalize Feedback: While AI can provide foundational feedback, students still need human connection and personalized insights. Use the time saved by AI to add qualitative comments that address higher-order thinking, creativity, and individual student growth.
- Not Explaining AI Usage to Students: Transparency is key. Inform students that AI is being used for grading, how it works, and what its limitations are. This helps manage expectations and fosters trust.
- Over-Automating Complex Assessments: For assignments that require deep critical thinking, creativity, or nuanced interpretation, a solely AI-driven grade may fall short. Use AI as a first pass, but ensure substantial human review for these complex tasks.
- Skipping Training and Support: Like any new technology, AI grading software requires a learning curve. Don’t expect instant mastery. Invest time in training yourself and utilizing support resources to fully leverage the tool’s capabilities.
Expert Tips & Best Practices for Maximizing AI Grading
To truly unlock the potential of AI grading software and transform your assessment practices, consider these expert tips and best practices. These strategies will help you integrate automated essay scoring tools and smart assessment solutions effectively into your classroom.
- Prioritize Rubric Development: Before using any AI grading tool, dedicate significant time to creating clear, measurable, and comprehensive rubrics. The AI’s effectiveness is directly tied to the quality of the criteria you provide.
- Start with Objective Assessments: Begin by using AI grading software for assignments with clear right/wrong answers, like quizzes or basic math problems. This builds confidence and familiarizes you with the tool’s capabilities before moving to more complex tasks.
- Use AI for First-Draft Feedback: For essays and projects, leverage AI to provide initial feedback on grammar, structure, and basic content alignment. This allows students to revise before you provide more in-depth, qualitative human feedback on higher-order thinking.
- Maintain Human Oversight: Always keep a “human-in-the-loop.” Review AI-generated grades and feedback, especially for subjective assignments. Your professional judgment is irreplaceable for understanding nuances, context, and individual student growth.
- Analyze AI-Generated Data: Don’t just look at individual grades. Use the analytics provided by AI grading software to identify class-wide strengths and weaknesses, common misconceptions, and areas where your instruction might need adjustment.
- Communicate with Students: Be transparent about your use of AI in grading. Explain to students how the tools work, what aspects are automated, and how you will use the AI’s output to inform your final assessment and feedback.
- Pilot and Iterate: Introduce AI grading gradually. Pilot it with a single assignment or class, gather feedback from students and colleagues, and then refine your approach. Learning and adaptation are key to successful integration.
- Seek Professional Development: Stay informed about the latest advancements and best practices in AI in education. Participate in workshops and webinars to enhance your understanding and skills in utilizing these tools effectively.
- Focus on Higher-Order Feedback: Reallocate the time saved from mechanical grading to providing richer, more meaningful feedback that encourages critical thinking, creativity, and deeper learning. This is where your true value as an educator shines.
“The most powerful aspect of AI grading software isn’t just efficiency; it’s the ability to transform the teacher’s role from a scorekeeper to a mentor, focusing on genuine learning and student development,” states Dr. Eliza Thornton, a leading expert in educational assessment technology. “Embrace it as a partner, not a replacement.”
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Grading Software
Q: What is AI grading software?
A: AI grading software uses artificial intelligence to automate the assessment of student assignments, from multiple-choice questions to essays. It helps teachers save time, provide consistent feedback, and analyze student performance more efficiently.
Q: How accurate are automated essay scoring tools?
A: Automated essay scoring tools have become highly sophisticated, often matching human grader consistency for specific criteria like grammar, mechanics, and structure. However, human review remains crucial for nuanced understanding, creative expression, and identifying complex errors beyond algorithmic detection.
Q: Can AI grading software detect plagiarism?
A: While some AI grading software platforms integrate plagiarism detection, it’s typically a separate functionality that checks for copied content against a vast database. Many tools primarily focus on evaluating content, structure, and grammar based on established rubrics, rather than directly identifying plagiarism.
Q: What are the privacy implications of using AI grading tools?
A: Privacy is a critical concern when using AI grading software. It’s essential to ensure that any tool complies with educational data privacy laws (like FERPA in the US or GDPR in Europe). Prioritize tools that anonymize data, have transparent privacy policies, and explicitly state that student data will not be used for purposes other than assessment and improving the educational experience.
Q: Is AI grading fair to all students?
A: AI grading software aims for objectivity by applying consistent rubrics to every submission. This can reduce human biases. However, potential algorithmic biases can exist if the AI’s training data is not diverse or representative. Teachers must monitor for such biases and use AI as a supportive tool alongside their human judgment to ensure equitable assessment.
Q: Can AI grading software be used for all subjects?
A: AI grading software is most mature for subjects with objective answers (math, science quizzes) and structured writing (essays where grammar, structure, and argument are key). For highly creative, artistic, or open-ended assignments, AI can provide preliminary insights, but human evaluation remains paramount for assessing originality and subjective quality.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Assessment
The evolution of AI grading software marks a significant turning point for educators in 2025. By providing automated essay scoring tools and intelligent assessment solutions, AI offers a powerful answer to the perennial challenge of grading workload. It not only saves teachers countless hours weekly but also enhances the consistency, speed, and analytical depth of feedback, ultimately fostering a more dynamic and responsive learning environment for students.
Embracing AI in assessment is not about diminishing the teacher’s role, but rather elevating it. By automating the mechanical aspects of grading, educators are freed to focus on their invaluable human skills: providing nuanced, empathetic feedback, addressing individual student needs, and inspiring deeper learning. The future of education is collaborative, with technology serving as a force multiplier for human pedagogical expertise. We encourage you to explore the diverse range of AI grading software available and discover how it can transform your assessment practices. For further reading on the impact of AI in various professional sectors, visit AI in Finance, or delve into the broader implications of AI in education on authoritative sites like Statista or academic resources via Google Scholar.
